| Is It Really Different This Time? |
| By John Mauldin |
Published
06/21/2009
|
Currency , Futures , Options , Stocks
|
Unrated
|
|
|
|
Is It Really Different This Time?
I have often written that the four most dangerous words in the investment world are "This Time It's Different." If memory serves me, I have written several e-letters disparaging various personages who have uttered those very words, and gone one to confirm later that it wasn't different. It almost never is. And yet - and yet! - I am going to make the case over the next few weeks that it really is different this time, with only a lonely asterisk as a caveat. What prompts my probable foolishness to tempt the investing gods is the rather large amount of bad analysis based on unreasonable (dare I say lazy or surface?) readings of statistics that is coming from the mainstream investment media and investment types with their built-in bias for bullish analysis. Normally, gentle reader, your humble analyst is a paragon of moderate sensibilities, but I have been pushed over a mental edge and need to restore balance. I anticipate that this topic will take several weeks, as trying to cover it all in one sitting would exhaust us both. It should be fun.
This Time It's Different*
Ben Bernanke's career will be analyzed and written about for many years. But the one thing that has caused me the most pain is his bringing of the term "green shoots" into the investment lexicon. These may be the two most overused and annoying words of my investment career. Every possible sign of a recovery is anointed with the phrase.
Of late, there has been a tendency for analysts to see numbers or statistics that are "less bad" and interpret them as signs that we are in recovery or at least almost there. They glance back at previous recoveries and say, "Doesn't this look like the last time? When such and such happens it means that recovery is on the way. We should therefore buy stocks" (or whatever).
That we are condemned to read such musings is part of the investment landscape. But that does not mean we shouldn't take the time to look at what the writer of those words is actually looking at. All too often of late, I find these people grasping at straws or failing to understand the data.
My premise for uttering the heresy "This Time It's Different*" is that the fundamental nature of the economic landscape has so changed that comparisons with post-WWII recoveries is at best problematical and at worst misleading.
As we will see next week, we are on a track that looks far more like the Great Depression than the recessions of our lifetimes. To expect a normal recovery cycle, whether it is corporate profits or lending or consumer spending or capital investment or (pick a category) is just not reasonable. This is a period that is fundamentally, in so many ways, different. And the recovery (and there will be one!) will also be of a different warp and woof throughout the entire world economy.
Let me see if I can summarize my thinking before we get into the reasoning behind it.
First, we are at the end of a huge cycle of increasing private debt that ended in an overleveraged society. The process of reducing debt and unwinding leverage is going to take a rather long time. It will not be the typical one or two years and then things get back to an ever-higher normal. We are, using a phrase coined by my friend Mohammed El Erian at PIMCO, on our way to a new normal. We are hitting a massive reset button on our economic world, taking us to some new and lower level of consumer spending, leverage, etc. No one knows what the new level will be, although admittedly we are closer to it than we were a year ago.
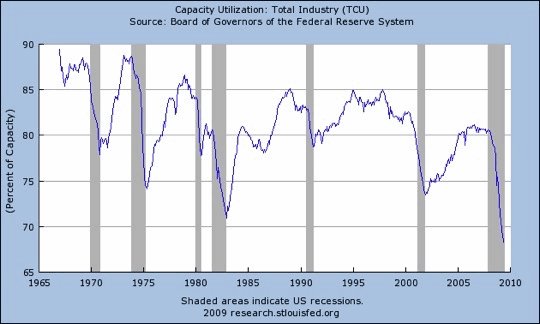
At this new normal, we will not need as many malls or factories or stores or new-car plants or car dealerships or any number of other things to satisfy the new normal of consumer desires. As an example, and jumping ahead to a statistic for one minute, capacity utilization is now approaching 65%. Anything under 80% is anemic. Does anyone really think that businesses (in general) are going to invest more money in expanding capacity, in the face of the lowest level of production relative to potential since the 1930s?
The savings rate has shot up from zero to 6% in just a very short time. It used to be 12%. It would not be all that unusual historically for savings to go to 9% or more in a few years. That means that consumer spending will drop by 9%. Since consumer spending was 70% of GDP, that new lower level will become our new normal. And of course, due to population growth and hopefully increasing incomes, consumer spending will once again grow from whatever that new normal will be. But it is going to take some time for spending to reach the level of our productive capacity of a few years ago. We are going to have to shutter a few factories and businesses.
David Rosenberg, now with Gluskin Sheff, offers us this insight:
"What really struck us in the employment report of a few weeks ago was the fact that the only segment of the population that is gaining jobs is the 55+ age category. This group gained 224,000 net new jobs in May while the rest of the population lost 661,000. In fact, over the last year, those folks 55 and up garnered 630,000 jobs whereas the other age categories collectively lost over six million positions. This is epic." [See chart below.]
"Moreover, the number of 55 year olds and up who have two jobs or more has risen 1.1% in the last year, the only age cohort to have managed to gain any multiple jobs at all. Remarkable. These folks have seen their wealth get destroyed by two bubble-busts less than seven years apart ... the Nasdaq nest egg back in 2001 and the 5,000 square foot McMansion in 2007. Both bubbles ended in tears ... and so close together."
As we will see, the housing market is going to take at least two more years to truly recover. Looking at one month's data that shows housing starts up a few thousand as a sign of recovery in the housing market is, well, silly. Housing starts are anemic and the inventory of unsold homes is still at all-time highs (a ten-month supply) with more and more homes coming onto the market through foreclosure.
The multiple causes of the recession are not subject to a quick fix. Offering to pay someone $4,500 to trade in an old car for a new one is a rather pathetic way to try and jump-start consumer spending and the auto industry. Is it not enough that we will "invest" $50 billion in GM, while shrinking the company to a size where it will be difficult for profits to ever pay back that investment? We have to add insult to injury and borrow more money to buy cars. Care to wager whether GM will need more money within five years? (And by the way, I love my GM (Cadillac) car, and will likely buy another one at some point, so I wish them well.)
The "stimulus plan" was ill-conceived and not very stimulative. But the combination of the Fed and Treasury and massive monetary infusions has pulled us back from the brink of Armageddon. But we are not out of the woods yet. There is much heavy lifting to be done on the way to the land of the new normal.
Welcome to the New Normal
Secondly, my premise is that the recovery is going to take longer and be much less robust than any recovery since WWII. With unemployment likely to go over 10%, and with our new normal world not needing as much production of so many things, unemployment is going to stay stubbornly higher for longer than in any previous recovery. We are going to look next week at a very sobering report from the San Francisco Fed that suggests we may be for a longer than usual jobless recovery.
Thirdly, all this is going to affect corporate profits, especially for companies that depend on consumer spending. Those investors who expect corporate profits to rebound in 2010 are likely to be disappointed. (For the record, if you go to the S&P web site, analysts are projecting anywhere from a 40% to a 60% rebound in earnings for 2010 for the S&P 500. I would willingly take the "under" on that bet if I could find any takers.) I think whatever profit recovery that is built into the market at today's prices is generous. It is going to be tough to get much of a return from traditional buy-and-hold equity index investing for some time.
Fourthly, this is a global problem and primarily one in the "developed" world. I think we will find that much of Europe will be in a worse state of affairs than the US. If there are bright spots in the developed world, I tend to think they will be Canada and Australia/New Zealand. The opportunities are more likely to be in emerging markets, after they adjust to the new normal.
What this all means is that we as investors, entrepreneurs, managers, employees, and consumers need to adjust our expectations. For those of us in the US, this is complicated significantly in that we really have no idea what new level of government spending and taxation we will be faced with in 2010 and beyond. For one of the few times in my life, what the government does is likely to have a huge impact on the economy, as there is the potential for a significant shift in the very fundamental nature of government involvement in the economy. It is difficult to see what the new normal will be.
In Continental Europe, your new normal is going to be further complicated by an eroding banking crisis that is likely to put a real crimp in any recovery. China and Asia must adjust to lower US consumer spending. They have built too many factories to supply what seemed like an inexhaustible US consumer. They have to find new internal markets or face their own new normal.
All that being said, at some point, perhaps as early as the third quarter, we could see a positive number for GDP, although I think it will be later. Part of the reason that we will see some positive numbers is that year-over-year comparisons are going to get easier to make. Last summer, when inflation was close to 5% and I was writing that deflation was the real danger, oil was rising from $40 to $160 and food prices were going through the roof. Now oil is back to $70 and so we get lower year-over-year inflation numbers. Over the last two years the price of oil/energy is up, but we measure inflation on a yearly basis.
Housing construction was once about 5% of GDP. Obviously, the collapse of housing construction has had a rather negative impact on recent GDP numbers. But housing is probably close to, if not at, a bottom. Even if it dropped by another 20%, it would have far less of an impact on GDP at the much-reduced level where it is now.
It is similar with inventories. They can only drop so much, and eventually they get to the new normal and stop being a drag on the statistical GDP. We are not in an unrelenting death spiral. There is a bottom. It is like a person jumping out of an airplane. They fall rather rapidly until the parachute opens, and as they get closer to the ground they manipulate the chute to further slow the descent. But until they reach the ground, they are still falling. That is the case today. The economy is still falling, but the parachute has opened. We are going to reach the bottom at some point. We will find that new normal. We just need to adjust our activities and plans around that new destination.
I truly believe we get back to 3% GDP growth and 4% unemployment at some point in the future, but it is going to be more than a few years, especially if taxes are raised as much as is talked about in some circles. But just as in the late '70s, when the outlook was not very bright, things will change for the better. When asked back then where the new jobs would come from, the correct answer was "I don't know, but they will come."
It is the same today. There are whole new technologies and industries that are going to be created in the next decade. Entrepreneurs will respond with new innovations and businesses. Jobs that are not now on the horizon will spring up.
As a society, we are having to work through the excesses of a lifestyle that was propped up by ever-increasing debt and an out-of-control consumerism. That will happen in the fullness of time. But it WILL take time, and we need to adjust our expectations to account for that.
Over the next few weeks, I am going to drill down into the data to show why recovery will take longer and to help you withstand what will be an onslaught of out-of-control bullishness over data that is simply less bad. Let's start with a few easy targets.
The Three Amigos
In 2001, I wrote about what I called the Three Amigos that I watched to give us an indication of the direction of the economy. They were capacity utilization, high-yield bonds, and the (now-renamed) ISM numbers. Watching the direction they go gives us a good idea where the economy is headed. I have not written about them for years (as a trio), so let's revisit our old friends. We saw above that capacity utilization is still in a cliff dive. For there to be an actual recovery, we need to see capacity utilization start to climb back up. That is not currently a very positive indicator.
Credit Spreads - Bullish or Bearish?
A number of commentators have been effusive about how credit spreads have "come back in." And indeed, junk-bond yields have fallen. That is a good thing. Look at the graph below (courtesy of Tony Boehk).
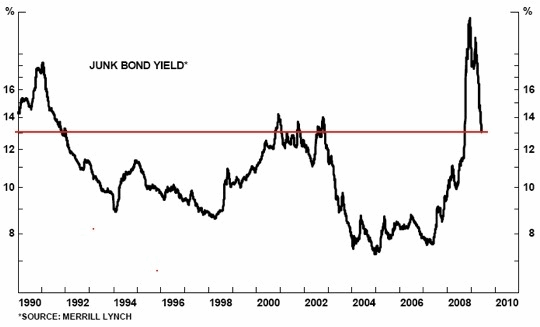
Note that yields have simply come down to levels associated with recessions, and not with actual recovery. What happened last year is that junk-bond yields priced in Armageddon. Now they simply price in a recession and slow recovery. Could they improve more? Certainly. But the easy lifting is done. The direction is right. Let's see how they do the next few months. If those yields keep falling, that would be a very positive sign.
ISM - Is Less Bad That Good?
The Institute for Supply Management released their data for May, and again, commentators were enthusiastic about the increase in the manufacturing index. Green shoots and other signs and wonders were all over the media.
The ISM is a survey of manufacturers about how their businesses are doing. They are surveyed on ten criteria, like new orders, employment, inventories, backlog of orders, etc. (for the full report, you can go to http://www.ism.ws/ISMReport/MfgROB.cfm?navItemNumber=12942).
From these responses the ISM creates an index. An index number above 50 means that the manufacturing sector is growing, and below 50 means it is shrinking. At the web site above, you can get quite a bit of detail. It is quite true that we have come back from what was the lowest overall index number in 30 years. But we are simply back to the level that was the low in the previous two recessions. The ISM number is "less bad" and that is a good thing, but it is still a bad number. Yes, it is headed in the right direction. Let's look at the actual chart.
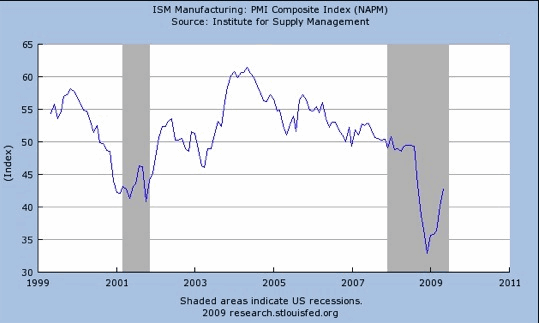
Of course, as businesses adjust to the new normal, whatever that level is, year-over-year comparisons will start to be positive. Simplistically, if a business makes 500 widgets a month and sales fall to 300, they will likely report falling production and rising inventories. Over time, inventories will finally settle out as management adjusts, and at some point inventories and production will (hopefully) start to rise. This gets reported as positive. The actual numbers may be down from the peak, but the direction of the company is once again on a positive slope.
When you look at the actual numbers comprising the release, the manufacturing part of the US economy is still contracting. Is it less bad than a few quarters ago? Yes, but it is still bad. The recent number is only slightly higher than the average for the last 12 months. We need this number to be above 50 to talk about an actual recovery in the here and now, as opposed to the future.
Contain Your Enthusiasm
Shipping containers moving into US ports rose by 2% in April, from March. That was cause for celebration in some circles. Buried way down, if mentioned at all, was the fact that compared to a year ago shipping is down 22%. And year-over-year comparisons have been worse for 22 months in a row. At some point, you get to a bottom. We find the new normal. But if the new normal is down 20%, that is a different-looking economy.
This quote came from good friend Dennis Gartman:
"'Stuff' moves by air when it is needed swiftly, but we can compare year-on-year data to get an idea of the relative weakness or strength of the economy. At the moment, the data is still very, very weak. According to the data reported out by the International Air Transport Association, after having touched just barely under $60 billion in '07 and '08, this year the IATA 'guesstimates' that only $40-$42 billion will move into the US.
"We are effectively back to the levels of '00-'04 and we are well below anything since '05. Having reached its worst year-on-year comparison back in December of last year when there was 23% air-transported cargo moving into the US from abroad, these yearly comparisons have remained about 20% lower since. Inventories of 'goods' on the nation's shelves remain high, and so long as that is true then we are going to see horrid, recessionary year-on-year comparisons in this very timely data."
Dennis also looked at rail shipments: "Since the start of this year this year, when the year-on year comparison was a relatively tepid -8%, the trend has been steadily 'from the upper left to the lower right' on the charts. By March, the year-on-year comparisons were averaging -15%. By April, -22%; by May -25%; and now, after a week or two of June, they are -26%. This is not a trend to be tampered with; this is a trend of some very real severity, and for now we fear that it is a trend rather firmly intact. Thankfully, it looks back, not forward; but if the past is prologue to the future, the future still looks rather bleak.
"Finally, there is a glimmering of hope on the rail horizon, and that is that the June figures, as they are compiled, are showing some signs of life. According to the AAR, 'freight traffic on US railroads during the week ended June 13 continued to show signs of gradual improvement ... [as] rail car loadings and intermodal were up from the previous week with carloads at their highest level in 10 weeks.'"
Welcome to the new normal. It is a quite distinctively different world than that of 2006. Global trade is off 10% and there is outright deflation in many places. We will have lots of data to look at over the next few weeks as we explore the new normal, but that is enough for today.
Oh, I almost forgot. The asterisk on "This Time It's Different*"? Human nature hasn't changed. We are still driven by fear and greed. The business cycle has not been repealed. Free-market capitalism will get us back (with a few new rules of engagement). What's different will be the nature of this recovery. All the other eternal truths will remain.
John Mauldin is president of Millennium Wave Advisors, LLC, a registered investment advisor. Contact John at John@FrontlineThoughts.com.
Disclaimer
John Mauldin is president of Millennium Wave Advisors, LLC, a registered investment advisor. All material presented herein is believed to be reliable but we cannot attest to its accuracy. Investment recommendations may change and readers are urged to check with their investment counselors before making any investment decisions.
|
|